What Is Satellite Dna Class 12

Coding sequences are known as genes.
What is satellite dna class 12. Molecular basis of inheritance class 12 biology mcqs pdf. Their characteristic that makes them useful for identification is that. This structure is described as a double helix as illustrated in the figure above. Dna fingerprinting is a technique that shows the genetic makeup of living things.
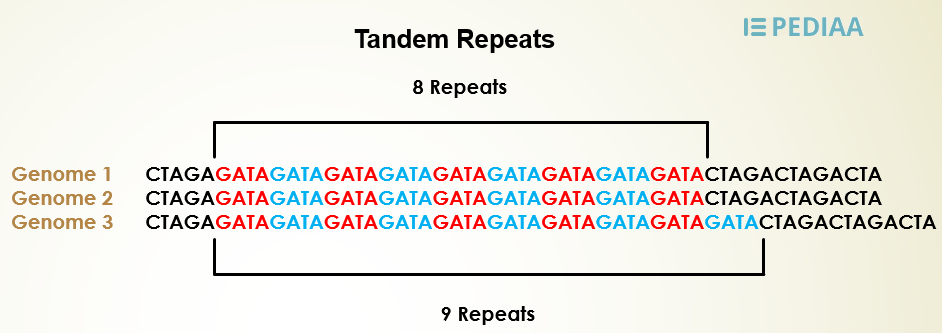
These can be few base pairs to hundreds or thousands of base pairs long. Satellite dna regions are stretches of repetitive dna which do not code for any specific protein. Dna satellites are of two types i e. The variation between individuals in the lengths of their dna satellites forms the basis of dna fingerprinting.
It is a nucleic acid and all nucleic acids are made up of nucleotides the dna molecule is composed of units called. Satellites are short sequences of dna repeated again and again to form long sequences. Students can solve ncert class 12 biology molecular basis of inheritance mcqs pdf with answers to know their preparation level. Variation in the lengths of these satellite dna is unique to every human being.
I differences between repetitive dna and satellite dna are. It is a method of finding the difference between the satellite dna regions in the genome what is dna fingerprinting. Key difference repetitive dna vs satellite dna genomic dna is mainly composed of coding dna and noncoding dna. Repetitive dna is the nucleotide sequences repeating over and over again in the genome of the organisms.
Satellite dna consists of very large arrays of tandemly repeating non coding dna satellite dna is the main component of functional centromeres and form the main structural constituent of heterochromatin. Satellite dna are dna sequences that contain highly repetitive dna. In cscl density gradient analysis they appear as light bands. It is the non coding dna with multiple copies of identical sequences which may lie in tandem or interspersed.
Satellite dna is a type of repetitive dna and it classified into minisatellites microsatellites and minivariant repeats based on the number of repetitive units the number of base pairs in each unit and the base composition of the units. Dna fingerprinting is the method followed by scientists to identify particular individuals as per their dna map. Thousands of genes are located on chromosomes repetitive dna introns and regulatory sequences are considered as noncoding dna in the genome. The name satellite dna refers to the phenomenon that repetitions of a short dna sequence tend to produce a different frequency of the bases adenine cytosine guanine and thymine and.
The dna structure can be thought of like a twisted ladder. In a dna strand the nucleotides are linked together by a glycosidic bonds b phosphodiester bonds c peptide bonds d hydorgen bonds. This has been helpful in dna fingerprinting.